skm alternatives and similar packages
Based on the "DevOps Tools" category.
Alternatively, view skm alternatives based on common mentions on social networks and blogs.
-
Moby
The Moby Project - a collaborative project for the container ecosystem to assemble container-based systems -
Gitea
Git with a cup of tea! Painless self-hosted all-in-one software development service, including Git hosting, code review, team collaboration, package registry and CI/CD -
Packer
Packer is a tool for creating identical machine images for multiple platforms from a single source configuration. -
kubeshark
The API traffic analyzer for Kubernetes providing real-time K8s protocol-level visibility, capturing and monitoring all traffic and payloads going in, out and across containers, pods, nodes and clusters. Inspired by Wireshark, purposely built for Kubernetes -
Ddosify
Effortless Kubernetes Monitoring and Performance Testing. Available on CLI, Self-Hosted, and Cloud -
Mizu
The API traffic viewer for Kubernetes providing deep visibility into all API traffic and payloads going in, out and across containers and pods inside a Kubernetes cluster. Think TCPDump and Wireshark re-invented for Kubernetes [Moved to: https://github.com/kubeshark/kubeshark] -
dasel
Select, put and delete data from JSON, TOML, YAML, XML and CSV files with a single tool. Supports conversion between formats and can be used as a Go package. -
Pomerium
Pomerium is an identity and context-aware reverse proxy for zero-trust access to web applications and services. -
Fleet device management
Open-source platform for IT, security, and infrastructure teams. (Linux, macOS, Chrome, Windows, cloud, data center) -
StatusOK
Monitor your Website and APIs from your Computer. Get Notified through Slack, E-mail when your server is down or response time is more than expected. -
s3gof3r
Fast, concurrent, streaming access to Amazon S3, including gof3r, a CLI. http://godoc.org/github.com/rlmcpherson/s3gof3r -
uTask
µTask is an automation engine that models and executes business processes declared in yaml. ✏️📋
InfluxDB - Power Real-Time Data Analytics at Scale

Do you think we are missing an alternative of skm or a related project?
Popular Comparisons
README
SKM is a simple and powerful SSH Keys Manager. It helps you to manage your multiple SSH keys easily!
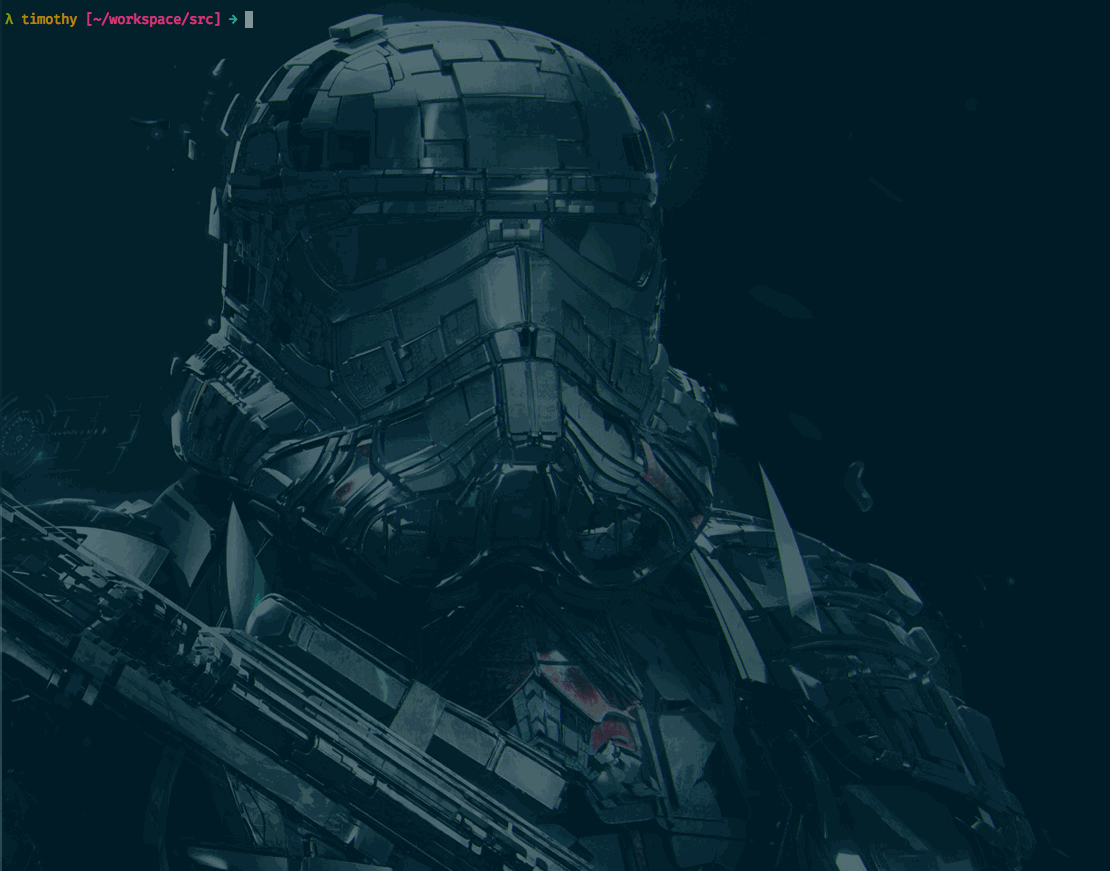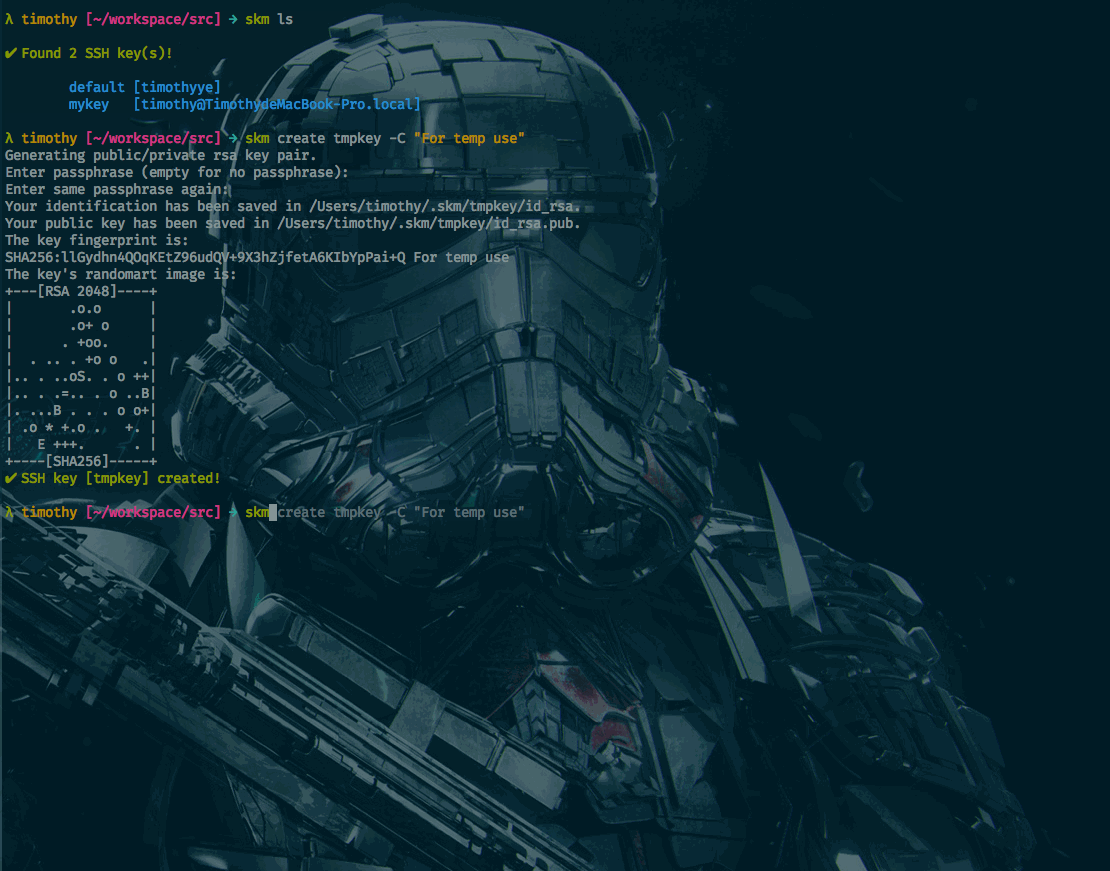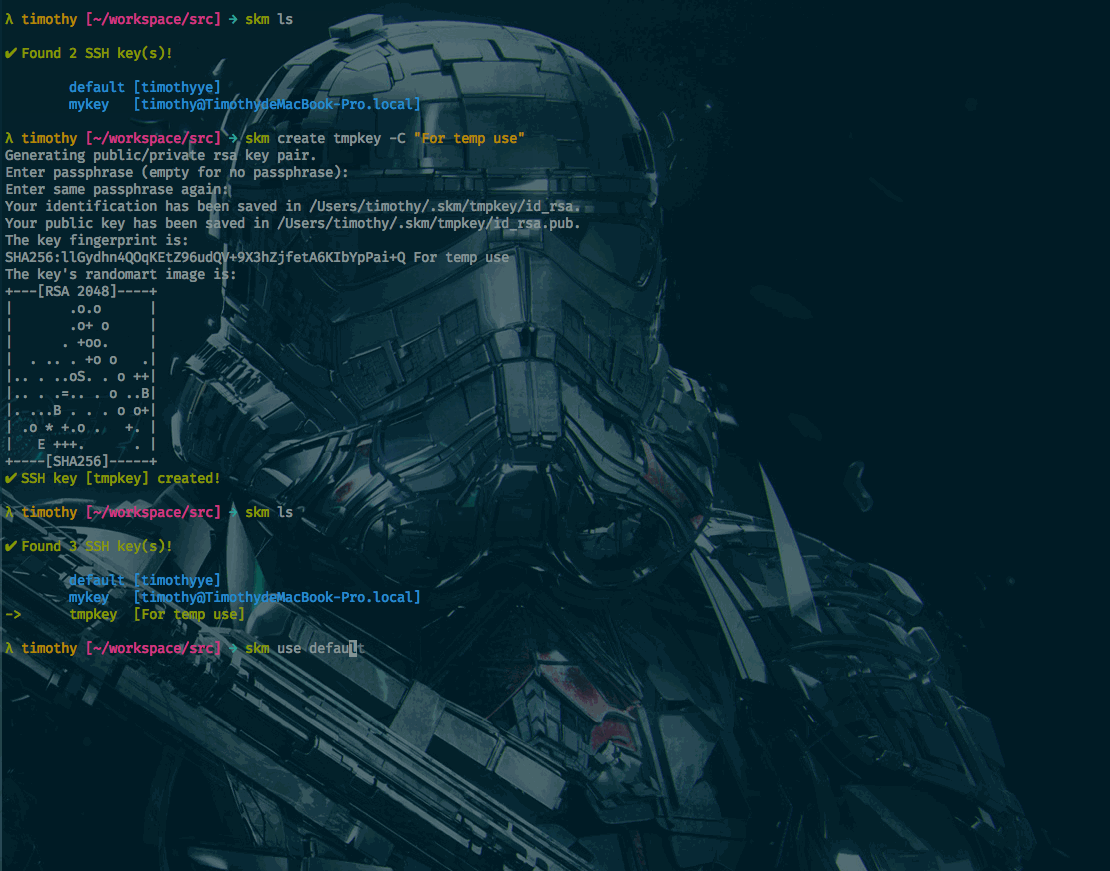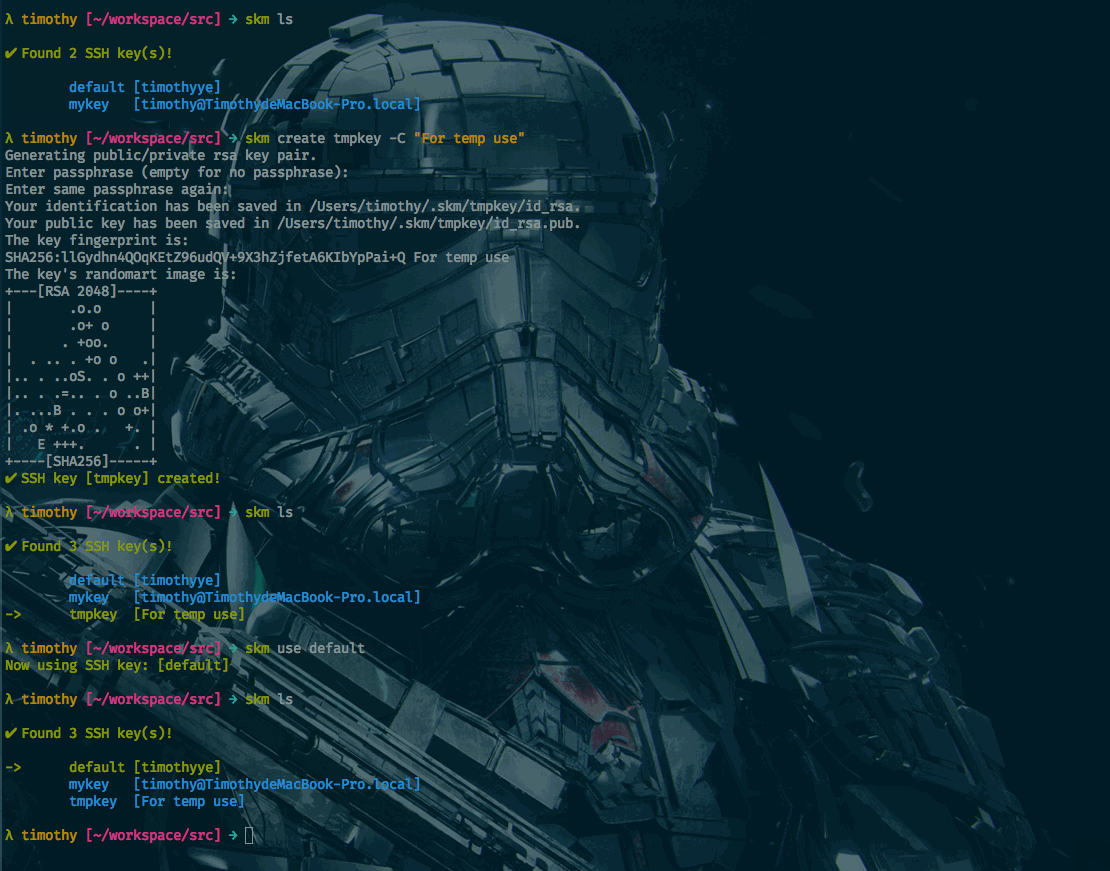
Features
- Create, List, Delete your SSH key(s)
- Manage all your SSH keys by alias names
- Choose and set a default SSH key
- Display public key via alias name
- Copy default SSH key to a remote host
- Rename SSH key alias name
- Backup and restore all your SSH keys
- Prompt UI for SSH key selection
- Customized SSH key store path
Installation
Homebrew
brew tap timothyye/tap
brew install timothyye/tap/skm
Using Go
go get github.com/TimothyYe/skm/cmd/skm
Manual Installation
Download it from releases and extact it to /usr/bin or your PATH directory.
Usage
% skm
SKM V0.8.5
https://github.com/TimothyYe/skm
NAME:
SKM - Manage your multiple SSH keys easily
USAGE:
skm [global options] command [command options] [arguments...]
VERSION:
0.8.5
COMMANDS:
init, i Initialize SSH keys store for the first time usage.
create, c Create a new SSH key.
ls, l List all the available SSH keys.
use, u Set specific SSH key as default by its alias name.
delete, d Delete specific SSH key by alias name.
rename, rn Rename SSH key alias name to a new one.
copy, cp Copy current SSH public key to a remote host.
display, dp Display the current SSH public key or specific SSH public key by alias name.
backup, b Backup all SSH keys to an archive file.
restore, r Restore SSH keys from an existing archive file.
cache Add your SSH to SSH agent cache via alias name.
help, h Shows a list of commands or help for one command.
GLOBAL OPTIONS:
--store-path value Path where SKM should store its profiles (default: "/Users/timothy/.skm")
--ssh-path value Path to a .ssh folder (default: "/Users/timothy/.ssh")
--restic-path value Path to the restic binary
--help, -h show help
--version, -v print the version
For the first time use
You should initialize the SSH key store for the first time use:
% skm init
✔ SSH key store initialized!
So, where are my SSH keys?
SKM will create SSH key store at $HOME/.skm and put all the SSH keys in it.
NOTE: If you already have id_rsa & id_rsa.pub key pairs in $HOME/.ssh, SKM will move them to $HOME/.skm/default
Create a new SSH key
NOTE: Currently ONLY RSA and ED25519 keys are supported!
skm create prod -C "[email protected]"
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /Users/timothy/.skm/prod/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /Users/timothy/.skm/prod/id_rsa.pub.
...
✔ SSH key [prod] created!
List SSH keys
% skm ls
✔ Found 3 SSH key(s)!
-> default
dev
prod
Set default SSH key
% skm use dev
Now using SSH key: dev
Prompt UI for key selection
You can just type skm use, then a prompt UI will help you to choose the right SSH key:

Display public key
% skm display
Or display specific SSH public key by alias name:
% skm display prod
Delete a SSH key
% skm delete prod
Please confirm to delete SSH key [prod] [y/n]: y
✔ SSH key [prod] deleted!
Copy SSH public key to a remote host
% skm cp [email protected]
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/Users/timothy/.skm/default/id_rsa.pub"
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
[email protected]'s password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '[email protected]'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
✔ Current SSH key already copied to remote host
Rename a SSH key with a new alias name
% skm rn test tmp
✔ SSH key [test] renamed to [tmp]
Backup SSH keys
Backup all your SSH keys to $HOME directory by default.
% skm backup
a .
a ./test
a ./default
a ./dev
a ./dev/id_rsa
a ./dev/id_rsa.pub
a ./default/id_rsa
a ./default/id_rsa.pub
a ./test/id_rsa
a ./test/id_rsa.pub
✔ All SSH keys backup to: /Users/timothy/skm-20171016170707.tar
If you have restic installed then you can also use that to create backups of your SKM store:
# First, you need a password for your repository
% if [[ ! -f ~/.skm-backups.passwd ]]; then
% openssl rand -hex 64 > ~/.skm-backups.passwd
% fi
% skm backup --restic
repository ... opened successfully, password is correct
Files: 0 new, 1 changed, 4 unmodified
Dirs: 0 new, 0 changed, 0 unmodified
Added to the repo: 1.179 KiB
processed 5 files, 2.593 KiB in 0:00
snapshot $SNAPSHOT saved
✔ Backup to /Users/$USER/.skm-backups complete
Restore SSH keys
% skm restore ~/skm-20171016172828.tar.gz
x ./
x ./test/
x ./default/
x ./dev/
x ./dev/id_rsa
x ./dev/id_rsa.pub
x ./default/._id_rsa
x ./default/id_rsa
x ./default/._id_rsa.pub
x ./default/id_rsa.pub
x ./test/id_rsa
x ./test/id_rsa.pub
✔ All SSH keys restored to /Users/timothy/.skm
Again, SKM also supports restic to create and restore backups:
% skm restore --restic --restic-snapshot $SNAPSHOT
repository $REPO opened successfully, password is correct
restoring <Snapshot $SNAPSHOT of [/Users/$USER/.skm] at 2018-10-03 19:40:33.333130348 +0200 CEST by $USER@$HOST> to /Users/$USER/.skm
✔ Backup restored to /Users/$USER/.skm
Integrate with SSH agent
You can use cache command to cache your SSH key into SSH agent's cache via SSH alias name.
Cache your SSH key
λ tim [~/]
→ skm cache --add my
Enter passphrase for /Users/timothy/.skm/my/id_rsa:
Identity added: /Users/timothy/.skm/my/id_rsa (/Users/timothy/.skm/my/id_rsa)
✔ SSH key [my] already added into cache
Remove your SSH key from cache
λ tim [~/]
→ ./skm cache --del my
Identity removed: /Users/timothy/.skm/my/id_rsa (MyKEY)
✔ SSH key [my] removed from cache
List your cached SSH keys from SSH agent
λ tim [~/]
→ ./skm cache --list
2048 SHA256:qAVcwc0tdUOCjH3sTskwxAmfMQiL2sKtfPBXFnUoZHQ /Users/timothy/.skm/my/id_rsa (RSA)
Customized SSH key store path
By default, SKM uses $HOME/.skm as the default path of SSH key store.
You can define your customized key store path in your ~/.bashrc or ~/.zshrc by adding:
SKM_STORE_PATH=/usr/local/.skm
Hook mechanism
Edit and place a executable file named hook at the specified key directory, for example:
~/.skm/prod/hook
This hook file can be both an executable binary file or an executable script file.
SKM will call this hook file after switching default SSH key to it, you can do some stuff in this hook file.
For example, if you want to use different git username & email after you switch to use a different SSH key, you can create one hook file, and put shell commands in it:
#!/bin/bash
git config --global user.name "YourNewName"
git config --global user.email "[email protected]"
Then make this hook file executable:
chmod +x hook
SKM will call this hook file and change git global settings for you!
Licence
*Note that all licence references and agreements mentioned in the skm README section above
are relevant to that project's source code only.


 ][6]
][6] -blue.svg)
