octillery alternatives and similar packages
Based on the "Database" category.
Alternatively, view octillery alternatives based on common mentions on social networks and blogs.
-
tidb
TiDB is an open-source, cloud-native, distributed, MySQL-Compatible database for elastic scale and real-time analytics. Try AI-powered Chat2Query free at : https://tidbcloud.com/free-trial -
TinyGo
Go compiler for small places. Microcontrollers, WebAssembly (WASM/WASI), and command-line tools. Based on LLVM. -
groupcache
groupcache is a caching and cache-filling library, intended as a replacement for memcached in many cases. -
bytebase
The GitLab/GitHub for database DevOps. World's most advanced database DevOps and CI/CD for Developer, DBA and Platform Engineering teams. -
go-cache
An in-memory key:value store/cache (similar to Memcached) library for Go, suitable for single-machine applications. -
immudb
immudb - immutable database based on zero trust, SQL/Key-Value/Document model, tamperproof, data change history -
buntdb
BuntDB is an embeddable, in-memory key/value database for Go with custom indexing and geospatial support -
pREST
PostgreSQL ➕ REST, low-code, simplify and accelerate development, ⚡ instant, realtime, high-performance on any Postgres application, existing or new -
xo
Command line tool to generate idiomatic Go code for SQL databases supporting PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQLite, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server -
nutsdb
A simple, fast, embeddable, persistent key/value store written in pure Go. It supports fully serializable transactions and many data structures such as list, set, sorted set. -
gocraft/dbr (database records)
Additions to Go's database/sql for super fast performance and convenience. -
lotusdb
Most advanced key-value database written in Go, extremely fast, compatible with LSM tree and B+ tree.
WorkOS - The modern identity platform for B2B SaaS

Do you think we are missing an alternative of octillery or a related project?
Popular Comparisons
README
Octillery 



Octillery is a Go package for sharding databases.
It can use with every OR Mapping library ( xorm , gorp , gorm , dbr ...) implementing database/sql interface, or raw SQL.
Currently supports MySQL (for product) and SQLite3 (for testing) .
Motivation
We need database sharding library in Go. Of course, we know some libraries like ( https://github.com/evalphobia/wizard , https://github.com/go-pg/sharding ). But OR Mapping library they support are restricted and we want to write sharding configuration declaratively, also expect to pluggable for sharding algorithm or database adapter, and expect to configurable sharding key or whether use sequencer or not.
Features
- Supports every OR Mapping library implementing
database/sqlinterface (xorm,gorp,gorm,dbr, ... ) - Supports using
database/sql( raw SQL ) directly - Pluggable sharding algorithm ( preinstalled algorithms are
moduloandhashmap) - Pluggable database adapter ( preinstalled adapters are
mysqlandsqlite3) - Declarative describing for sharding configuration in
YAML - Configurable sharding algorithm, database adapter, sharding key, whether use sequencer or not.
- Supports capture read/write queries just before passing to database driver
- Supports database migration by CLI ( powered by
schemalex) - Supports import seeds from CSV
Install
Install as a CLI tool
go get go.knocknote.io/octillery/cmd/octillery
Install as a library
go get go.knocknote.io/octillery
How It Works
1. How database sharding works
We explain by using posts table.
posts table schema is
CREATE TABLE `posts` (
`id` bigint unsigned NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`user_id` bigint unsigned NOT NULL,
`created_at` datetime NOT NULL,
`updated_at` datetime NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `uq_posts_01` (`user_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4;
And we want to shard this table to four databases for load distribution.
In this case, we can try to two approach according to requirements.
1. Using Sequencer
If you want id to be unique in all databases, you should use this approach.
Architecture of this approach would be the following.
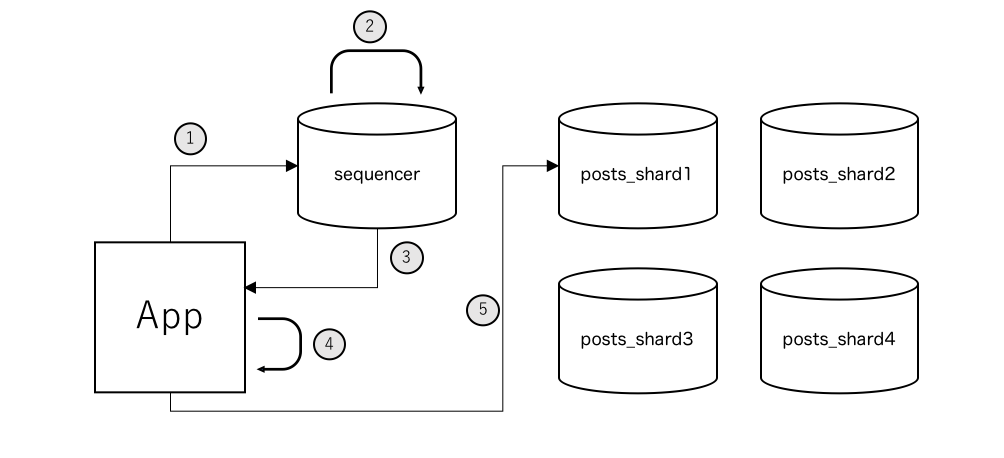
Application create SQL ( like insert into posts (id, user_id, ...) values (null, 1, ...) ), in this point, id value is null because still not decide. In accordance with the above graph, insert this query to one of the databases.
- Application requests id value to sequencer
- Sequencer generates next unique id in all shards
- Sequencer returns id value to application ( ex.
id = 1) - Replace
idvalue fromnullto1(ex.insert into posts (id, user_id, ...) values (1, 1, ...)) - Decide target based of
idvalue by sharding algorithm ( defaultmodulo) and insert record to selected database.
By using sequencer approach, you can get unique id value in all databases.
Therefore, if you insert multiple records, database records should looks like the following.
posts_shard_1 posts_shard_2 posts_shard_3 posts_shard_4 id user_id id user_id id user_id id user_id 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 7 8 8
2. Using Sharding Key ( without Sequencer )
If you don't care about uniqueness of id, you can use sharding key approach.
Architecture of this appraoch would be the following.
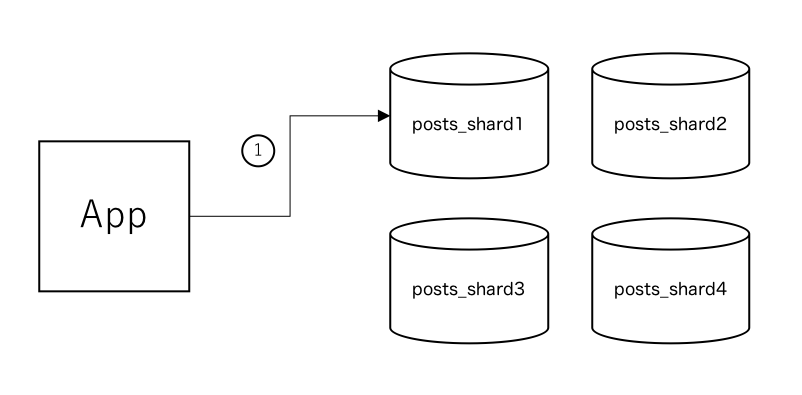
- Decide target based of
user_idvalue by sharding algorithm ( defaultmodulo) and insert record to selected database.
By using sharding key approach, same id value will appear in multiple databases. Therefore, if you insert multiple records, database record should looks like the following.
posts_shard_1 posts_shard_2 posts_shard_3 posts_shard_4 id user_id id user_id id user_id id user_id 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 5 2 6 2 7 2 8
2. Requirements of database sharding library
We explained how to sharding database at section 1. From this we define requirements of database sharding library.
- Know about database sharding configuration
- Capture query just before passing to database driver
- Parse query and find sharding key
- If use sequencer, requests
idvalue to sequencer and replace value ofidcolumn by it - Select sharding target based of sharding key by sharding algorithm
3. How Octillery works
How To Capture Query
Octillery CLI tool supports transpose command.
It replace import statement of database/sql to go.knocknote.io/octillery/database/sql.
go.knocknote.io/octillery/database/sql package has compatible interface of database/sql.
Therefore, OR Mapping library call Octillery's interface. and it can capture all queries.
How To Parse SQL
Octillery use github.com/blastrain/vitess-sqlparser as SQL parser. It implements powered by vitess and tidb .
How To Use New Database Adapter
Octillery supports mysql and sqlite3 adapter by default.
If you want to use new database adapter, need to the following two steps.
- Write
DBAdapterinterface. ( see https://godoc.org/go.knocknote.io/octillery/connection/adapter ) - Put new adapter file to
go.knocknote.io/octillery/plugindirectory
How To Use New Database Sharding Algorithm
Octillery supports modulo and hashmap algorithm by default.
If you want to use new algorithm, need to the following two steps.
- Write
ShardingAlgorithminterface. ( see https://godoc.org/go.knocknote.io/octillery/algorithm ) - Put new algorithm file to
go.knocknote.io/octillery/algorithmdirectory
Usage
1. Install CLI tool
$ go get go.knocknote.io/octillery/cmd/octillery
2. Install library
$ go get go.knocknote.io/octillery
3. Replace already imported database/sql statement
$ octillery transpose
※ --dry-run option confirms without overwriting
4. Install database adapter
$ octillery install --mysql
5. Describe database cofiguration in YAML
databases.yml
default: &default
adapter: mysql
encoding: utf8mb4
username: root
master:
- localhost:3306
tables:
posts:
shard: true
shard_key: user_id
shards:
- post_shard_1:
<<: *default
database: posts_shard_1
- post_shard_2:
<<: *default
database: posts_shard_2
6. Migrate database
$ octillery migrate --config databases.yml /path/to/schema
※ --dry-run option confirms migration plan
7. Load configuration file
package main
import (
"go.knocknote.io/octillery"
"go.knocknote.io/octillery/database/sql"
)
func main() {
if err := octillery.LoadConfig("databases.yml"); err != nil {
panic(err)
}
db, _ := sql.Open("mysql", "")
db.QueryRow("...")
}
Document
See GoDoc
Development
Install dependencies
$ make deps
If update dependencies, the following
- Modify
glide.yaml - Run
make update-deps - Commit
glide.yamlandglide.lock
Run tests
$ make test
See also
sqlparser: https://github.com/blastrain/vitess-sqlparserschemalex: https://github.com/schemalex/schemalex
Committers
Masaaki Goshima (@goccy)
LICENSE
MIT
*Note that all licence references and agreements mentioned in the octillery README section above
are relevant to that project's source code only.

